What is gingivitis?
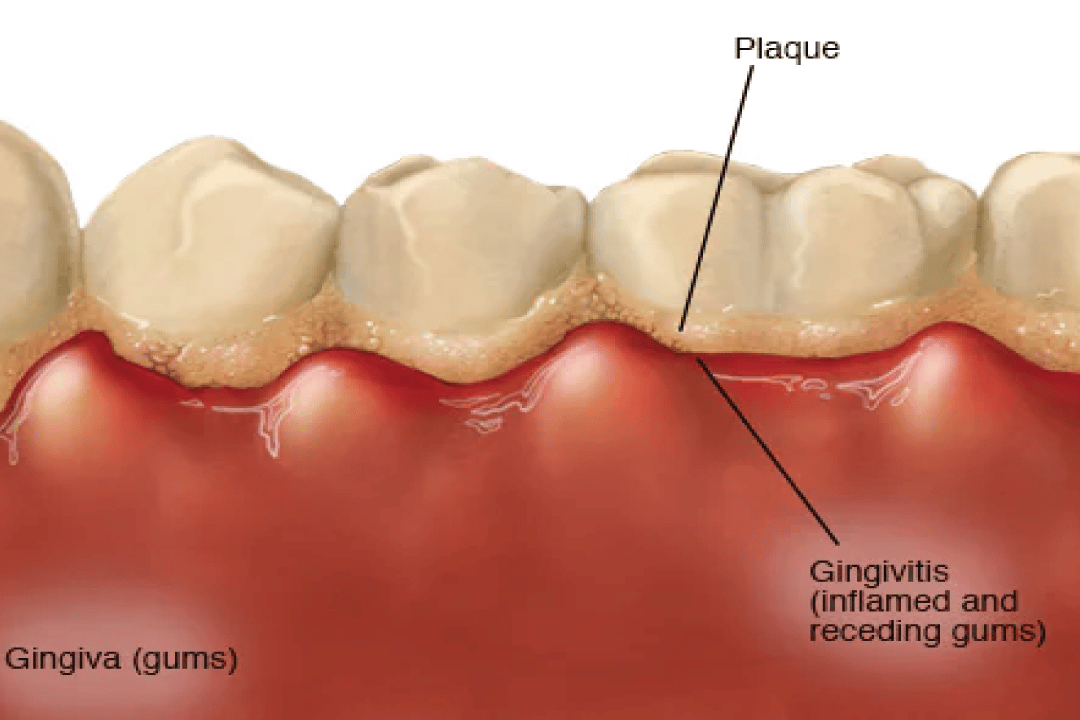
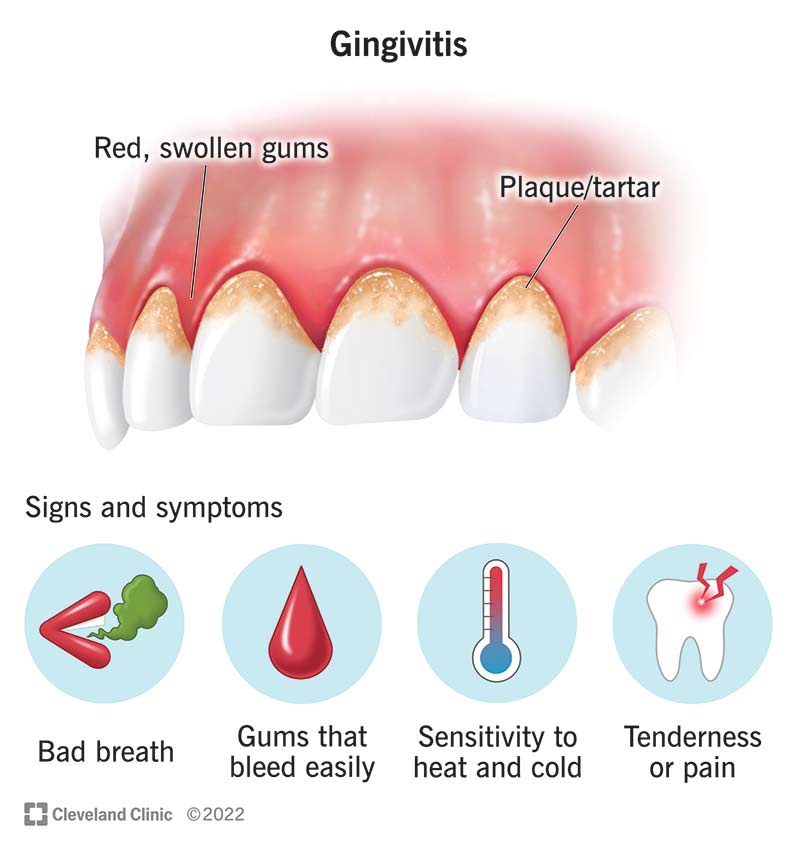
Gingivitis is a common inflammatory disease of the gums. This occurs when plaque and bacteria build up on the teeth and along the gum line, causing the gums to become red, swollen, and bleed easily. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a serious infection that can damage the tissues and bones that support the teeth.

Causes of gingivitis
The main cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene. When you don’t brush and floss your teeth regularly, plaque and bacteria can build up on your teeth and along the gum line. This sticky film irritates the gums and causes them to become inflamed. Other factors that can increase your risk of developing gingivitis include:
- Smoking
- Dry mouth
- Diabetes
- Certain medications
- Weak immune system
- Genetics

Symptoms of gingivitis
In the early stages, gingivitis may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, you may experience:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Receding gums
- Bad breath
- Loose teeth
- Tooth pain
Treatment for gingivitis
The goal of gingivitis treatment is to remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums and prevent the disease from progressing. Treatment for gingivitis typically includes:
- Professional dental cleaning: Your dentist or dental hygienist will remove plaque and tartar from your teeth and below the gum line.
- Good oral hygiene: You will need to brush your teeth twice a day and floss once a day to remove plaque and bacteria from your teeth and gums.
- Antibacterial mouthwash: Your dentist may recommend using an antibacterial mouthwash to help kill bacteria in your mouth.
- Lifestyle changes: You may also need to make lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and managing diabetes, to reduce your risk of developing gingivitis.
In some cases, more aggressive treatment may be needed, such as surgery to remove deep pockets of infection between the teeth and gums.
Prevention of gingivitis
The best way to prevent gingivitis is to practice good oral hygiene. This includes:
- Brushing your teeth twice a day for two minutes each time
- Flossing once a day
- Using an antibacterial mouthwash
- Seeing your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings
You can also reduce your risk of developing gingivitis by:
- Quitting smoking
- Managing diabetes
- Controlling dry mouth
- Getting regular checkups with your dentist
If you have any questions about gingivitis, please talk to your dentist.
Why does my tongue feel burned but isn’t?

Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a condition that causes a sensation of burning in the mouth. There are several known causes of BMS, but the reason for its onset can be unclear. Treatment may help improve symptoms over a period of weeks or months.
According to the American Academy of Oral Medicine (AAOM), approximately 2 percent of people in the United States have BMS. It can affect the following parts of the mouth:
- tongue
- the roof of the mouth
- inside of the cheeks
- gums
- lips
In this article, we look at the causes of a burning tongue and discuss home remedies and medical treatments for BMS.


MirageC/Getty Images
Some people with a burning tongue may have scalded their mouth with a hot drink or piece of food, in which case they do not have BMS.
The pain or discomfort of a minor physical burn may remain for several hours or more, but it will typically resolve without treatment.
Causes of BMS
True BMS is believed to be a type of neuropathic pain. It may be primary, meaning that it results from a direct cause, or secondary, which means that the cause is indirect.
According to the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, the primary form of BMS results from damage to the nerves that control taste and pain sensations.
Secondary BMS may occur because of other medical conditions or treatments, including:
- allergies to specific foods or dental products
- anxiety or depression
- diabetes
- dry mouth
- gastroesophageal reflux disease
- menopause
- geographic tongue
- an underactive thyroid, called hypothyroidism
- medications, such as high blood pressure medicines
- mouth infections
- nutritional deficiencies
Other secondary causes may include a person’s habits, such as:
- biting the tip of the tongue frequently
- consuming too many acidic foods or drinks
- grinding the teeth on a regular basis
- overbrushing the tongue
- overusing mouthwash or abrasive oral hygiene products
- wearing ill-fitting dentures
In many cases, the cause of BMS is unclear.
The symptoms of BMS, including a burning tongue, may:
- appear suddenly or develop over time
- come and go or remain constant
- be mild, moderate, or severe
- improve when eating or drinking
BMS commonly affects the tongue, but people may also experience discomfort in the:
- lips
- gums
- throat
- roof of the mouth
- inside of the cheeks
It is also possible to have symptoms that affect the whole mouth.
Common BMS symptoms include:
- a burning or scalding sensation in the mouth
- a bitter or metallic taste
- a dry mouth
- difficulty swallowing
- increased thirst
- loss of taste
What home remedies can help?
Many people can find relief by using home remedies, including the following:
Take fluids and ice
The pain of BMS sometimes improves when eating or drinking.
To alleviate symptoms, people can drink plenty of water and other fluids throughout the day or suck on ice chips.
Doing this will also reduce the sensation of dry mouth and may temporarily mask bad tastes.
Avoid problematic foods and drinks
Strong-tasting or harsh foods and beverages can irritate the mouth. Limiting or avoiding the following foods can be beneficial:
- acidic foods, such as tomatoes and citrus fruits
- acidic drinks, including citrus juices, sodas, and coffee
- alcohol and products containing alcohol
- spicy foods
- items containing cinnamon or mint, including herbal teas, candies, and baked goods
Change dental hygiene products and habits
Oral health products, including toothpaste and mouthwashes, can irritate the lining of the mouth.
It is advisable to use flavor-free toothpaste that is suitable for sensitive teeth and to limit the use of mouthwash.
Stopping other oral habits, such as biting the tip of the tongue, may also help.
Quit smoking
Smoking tobacco can irritate the delicate skin inside the mouth. It is best to avoid all products that contain tobacco to reduce or prevent BMS symptoms.
Address medical conditions
Several conditions contribute to BMS. People should discuss home remedies and medical treatments for these conditions with a doctor.
Controlling the underlying issue may improve symptoms.
Reduce stress
Stress, anxiety, and depression may cause or worsen the symptoms of BMS. In turn, BMS may increase stress levels because it affects a person’s quality of life.
People with BMS should try to reduce stress and seek help for other mental health issues where possible.
Seek support
It is not always possible to fully alleviate the symptoms of BMS, and some people will need to learn how to manage their discomfort. It can be helpful to seek support and advice from others, including a therapist or a chronic pain support group.
Risk factors for BMS include:
- Sex: According to the AAOM, females are up to seven times more likely to have BMS than males.
- Age: Older adults have a higher risk of BMS because they are more likely to wear dentures and have other underlying health issues.
- Being postmenopausal: People who have gone through menopause are more at risk. Researchers estimate that 18 to 33 percentTrusted Source of postmenopausal females have BMS.
Other risk factors include:
- having food allergies
- wearing dentures or undergoing dental work
- experiencing recent illness
- taking certain medications
- having specific medical conditions
- being stressed or anxious
BMS does not typically cause complications, but it is possible that people with the condition will experience:
- anxiety or depression
- difficulty eating or swallowing
- sleep problems
Individuals may be able to reduce their risk of BMS by:
- avoiding tobacco
- ensuring that dentures fit correctly
- limiting or avoiding alcohol and acidic foods and drinks
- managing other health conditions
- using oral hygiene products for sensitive teeth
There is no guaranteed way to prevent all cases of BMS.
Doctors usually diagnose BMS by ruling out other medical conditions.
There is no known cure for primary BMS, but treatment for secondary BMS generally focuses on managing the underlying condition. This treatment may include taking nutritional supplements or medications.
People may use the following to manage the pain of primary or secondary BMS:
- cognitive behavioral therapy
- oral rinses
- pain-relieving drugs
- saliva-replacement products
- specific antidepressants or anticonvulsant medications

The AAOM say that between one-half and two-thirds of people with BMS will experience some level of improvement in their burning tongue or other symptoms after a few weeks to several months of treatment.
People who have chronic BMS, which lasts for several years, are typically able to stabilize and manage their symptoms. Symptoms can sometimes spontaneously disappear.
There is no link between BMS and the development of oral cancer.
People should see a doctor or dentist to help them determine the underlying cause of their BMS and develop a treatment program for symptom relief.
































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(999x0:1001x2)/catherine-ohara-013026-7-4b5b413a646d4f15a1fd15ac8b933811.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)








