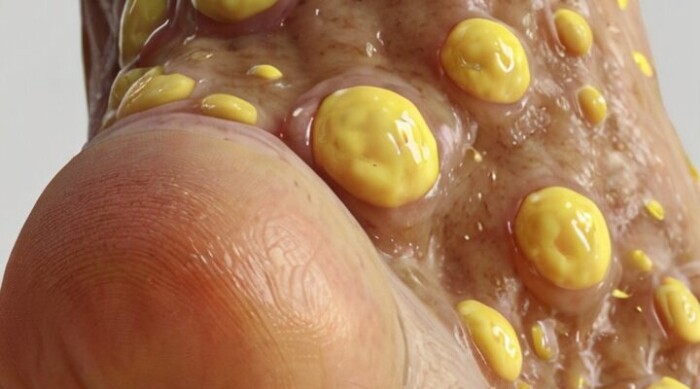
Overview
Athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) is a fungal skin infection that usually begins between the toes. It commonly occurs in people whose feet have become very sweaty while confined within tight-fitting shoes.
Signs and symptoms of athlete’s foot include an itchy, scaly rash. The condition is contagious and can be spread via contaminated floors, towels or clothing.
Athlete’s foot is closely related to other fungal infections such as ringworm and jock itch. It can be treated with antifungal medications, but the infection often comes back.

Symptoms
Athlete’s foot can affect one or both feet. Common signs and symptoms are:
- Scaly, peeling or cracked skin between the toes
- Itchiness, especially right after taking off shoes and socks
- Inflamed skin that might appear reddish, purplish or grayish, depending on your skin color
- Burning or stinging
- Blisters
- Dry, scaly skin on the bottom of the foot that extends up the side
When to see a doctor
If you have a rash on your foot that doesn’t improve within two weeks of beginning self-treatment with an over-the-counter antifungal product, see your doctor.
If you have diabetes, see your doctor if you suspect that you have athlete’s foot. Also see your doctor if you have signs of an infection — swelling of the affected area, pus, fever.

Causes
Athlete’s foot is caused by the same type of fungi (dermatophytes) that cause ringworm and jock itch. Damp socks and shoes and warm, humid conditions favor the organisms’ growth.
Athlete’s foot is contagious and can spread through contact with an infected person or from contact with contaminated surfaces, such as towels, floors and shoes. You can also spread it from the foot to other parts of the body, especially if you scratch or pick the infected parts of your foot.

Risk factors
You are at higher risk of athlete’s foot if you:
- Frequently wear enclosed footwear
- Sweat heavily
- Share mats, rugs, bed linens, clothes or shoes with someone who has a fungal infection
- Walk barefoot in public areas where the infection can spread, such as locker rooms, saunas, swimming pools, communal baths and showers
Complications
The athlete’s foot infection can spread to other warm, moist parts of the body. Jock itch is often caused by the same fungus that results in athlete’s foot. It’s common for the infection to spread from the feet to the groin because the fungus can travel on hands or towels.
Athlete’s foot can sometimes lead to bacterial infections.
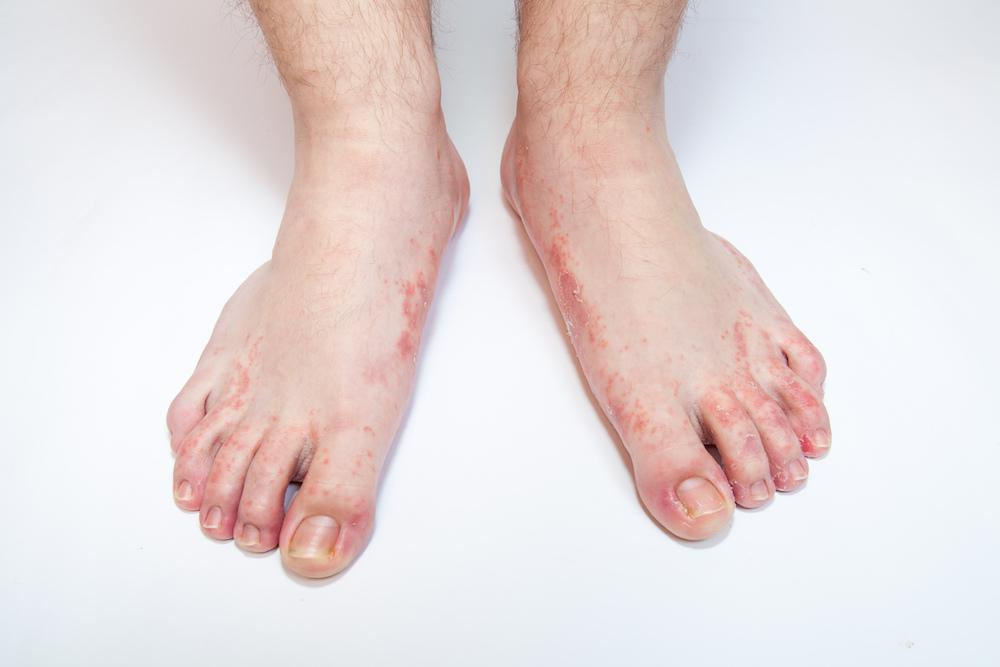
Prevention
These tips can help you avoid athlete’s foot or avoid spreading it to others:
- Let your feet air out. When you can, wear sandals to let your feet air out as much as possible.
- Wash your feet daily. Use warm, soapy water and rinse and dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes. Apply a medicated foot powder (Tinactin, Gold Bond, others) or other medicated powder (Lotrimin AF, Zeasorb, others) if you’re prone to athlete’s foot.
- Change socks regularly. Change your socks at least once a day — more often if your feet get really sweaty. Moisture-wicking socks, such as those made from cotton, help keep your feet drier than do nylon socks.
- Alternate pairs of shoes. Use different shoes from day to day. This gives your shoes time to dry after each use.
- Protect your feet in public places. Wear waterproof sandals or shoes around public pools, showers and lockers rooms.
- Be aware of the risk factors for spreading the condition. If you live with others, don’t share shoes or unwashed bedding and towels.


The 11 Best Foods for Healthy Skin

A diet rich in healthy fats and vitamins can support skin health. Many fruits and vegetables, including red grapes and tomatoes, contain compounds that can benefit your skin.
Nutrition is important for health. An unhealthy diet can damage your metabolism, cause weight gain, and even damage organs, such as your heart and liver.
What you eat also affects another organ — your skin.
As scientists learn more about diet and the body, it’s increasingly clear that what you eat can significantly affect the health and aging of your skin.
This article takes a look at 12 of the best foods for keeping your skin healthy.
omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for maintaining skin health.
Omega-3 fatty acids are necessary to help keep skin thick, supple, and moisturized. In fact, an omega-3 fatty acid deficiency can cause dry skin.
The omega-3 fats in fish reduce inflammation, which can cause redness and acne. They can even make your skin less sensitiveTrusted Source to the sun’s harmful UV rays.
Some studiesTrusted Source show that fish oil supplements may help fight inflammatory and autoimmune conditions affecting your skin, such as psoriasis and lupus.
Fatty fish is also a source of vitamin E, one of the most important antioxidants for your skin. Getting enough vitamin E is essential for helping protect your skin against damage from free radicals and inflammation.

2. Avocados
Avocados are high in healthy fats. These fats benefit many functions in your body, including the health of your skin.
A 2022 pilot studyTrusted Source involved healthy women consuming one avocado daily for 8 weeks. The researchers found that daily avocado consumption may may lead to enhanced elasticity and firmness of facial skin.
Avocados are also a good source of vitamin E, which is an important antioxidant that helps protect your skin from oxidative damage. Most Americans don’t get enough vitamin E through their diet.
Vitamin C is also essential for healthy skin. Your skin needs it to create collagen, which is the main structural protein that keeps your skin strong and healthy.
Vitamin C is also an antioxidant that helps protect your skin from oxidative damage caused by the sun and the environment, which can lead to signs of aging.
Walnuts have many characteristics that make them an excellent food for healthy skin.
They’re a good source of essential fatty acids, which are fats that your body cannot make itself.
ALA, omega-3 fats, magnesium, and the amino acid arginine — all of which are found in walnuts — may also decrease inflammationTrusted Source in your body, including your skin.
4. Sunflower seeds

In general, nuts and seeds are good sources of skin-boosting nutrients.
Sunflower seeds are an excellent example. They contain high levels of both monounsaturated and
omega-6 fats, and may help reduce inflammation and cholesterol levels.

Beta carotene is a nutrient found in plants. It functions as provitamin A, which means it can be converted into vitamin A in your body.
Beta carotene is found in oranges and vegetables such as carrots, spinach, and sweet potatoes.
Sweet potatoes are an excellent source — one 1/2-cup (100-gram) serving of baked sweet potato contains enough beta carotene to provide more than six times the DV of vitamin A.
Carotenoids like beta carotene help keep your skin healthy by acting as a natural sunblock. When consumed, this antioxidant is incorporated into your skin and helps protect your skin cells from sun exposure. This may help prevent sunburn, cell death, and dry, wrinkled skin.
vitamin C. This vitamin is necessary for creating the protein collagen, which keeps skin firm and strong.
Broccoli is full of many vitamins and minerals important for skin health, including zinc, vitamin A, and vitamin C.
It also contains lutein, a carotenoid that works like beta carotene. Lutein helps protect your skin from oxidative damage, which can cause your skin to become dry and wrinkled.
Broccoli florets also pack a special compound called sulforaphane, which boasts some impressive potential benefits. It may even have anti-cancer effects.
Sulforaphane is likewise a powerful protective agent against sun damage. It works in two ways: neutralizing harmful free radicals and switching on other protective systems in your body.
lycopene.
Beta carotene, lutein, and lycopene have been shown to protect your skin against damage from the sun. They may also help prevent wrinkling.
Because tomatoes are rich in carotenoids, they’re an excellent food for maintaining healthy skin.
Consider pairing carotenoid-rich foods like tomatoes with a source of fat, such as cheese or olive oil. Fat increases your absorption of carotenoids.
9. Dark chocolate
If you need another reason to eat chocolate, here it is: the effects of cocoa on your skin are pretty phenomenal.
After 6–12 weeks of consuming a cocoa powder high in antioxidants each day, participants in one study experienced thicker, more hydrated skin.
Their skin was also less rough and scaly, less sensitive to sunburn, and had better blood flow — which brings more nutrients to your skin.
Another study found that eating 20 grams of high-antioxidant dark chocolate per day could allow your skin to withstand over twice as much UV radiation before burning, compared with eating low-antioxidant chocolate.
Several other studies have observed similar results, including improvements in the appearance of wrinkles. However, keep in mind that at least one study didn’t find significant effects.
Make sure to choose dark chocolate with at least 70% cocoa to maximize the benefits and keep added sugar to a minimum.
green tea can help protect your skin against sun damage.
While green tea is a great choice for healthy skin, you may want to avoid drinking your tea with milk, as there’s evidence that milk could reduce the effect of green tea’s antioxidants.
resveratrol, a compound that comes from the grapes’ skin.
Resveratrol is credited with a wide range of health benefits, among them is reducing the effects of aging.
Test-tube studies suggest it may also help slow the production of harmful free radicals, which damage skin cells and cause signs of aging.
This beneficial compound is also found in red wine. Unfortunately, there’s not much evidence that the amount of resveratrol you get from a glass of red wine is enough to affect your skin.
And since red wine is an alcoholic beverage, there are negative effects to drinking it in excess.
It’s not recommended to start drinking red wine just because of its potential health benefits. Instead, you should increase your intake of red grapes and berries.

What you eat can significantly affect your skin health.
Make sure you’re getting enough essential nutrients to protect your skin. The foods on this list are great options to keep your skin healthy, strong, and attractive.


























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(754x379:756x381):format(webp)/chow-chow-bowling-green-subway-70ac9e829e20441a978d9f05a1085374.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(725x300:727x302):format(webp)/Bridget-Garrison-dogs-tally-karma-01-021926-5f803803830d4771a5d48258b325f341.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(749x0:751x2):format(webp)/Dog-missing-in-Colorados-mountains-for-43-days-reunited-with-owner-thanks-to-Summit-Lost-Pet-Rescue-022426-0ebb1d6502764f8eb20d846307727ad0.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(743x471:745x473):format(webp)/Abandoned-Dog-at-Airport-022126-d755d65eb323443bade62469ed85c911.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(749x0:751x2):format(webp)/rescued-dog-1-030226-b2d2c821a5d74691ba8edd4e8f76508d.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(1211x776:1213x778):format(webp)/cats-rescued-22626-91b98a0bd7254a93a6bbf1a223dac5b0.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(736x185:738x187):format(webp)/abandoned-puppies-01-021126-de716b3fef81415bb0669b390e8abddd.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(749x0:751x2)/Irish-setter-gives-birth-to-record-17-puppies-030326-43c2927d84ed4a59880b16c2c8fdd530.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(899x646:901x648)/Tatiana-Schlossberg-Jack-Schlossberg-030126-02-ffbc8841a935444d9a68bdeab3cfe504.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)
