
Diabetes is a serious condition that can develop gradually, often without obvious symptoms in the early stages. Many people experience warning signs but dismiss them as minor health problems. Recognizing these subtle clues can be crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we’ll explore 10+ symptoms that, if understood, can help you take action before the condition progresses.
CONTENT IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED TO BE A SUBSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL ADVICE.
SEEK THE ADVICE OF YOUR PHYSICIAN REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.
Mood Changes and Irritability

There is emerging research suggesting that fluctuations in blood sugar levels can affect mood and cognitive function. For instance, studies have observed that sudden changes in blood glucose may be linked to irritability, anxiety, or even aggression. However, these symptoms are nonspecific and can be attributed to many other causes such as stress or lack of sleep. They may serve as a supplementary clue but are not diagnostic on their own.
Darker Area of Skin

A dark, velvety patch of skin that appears on the neck, armpits, groin, or elsewhere may be a sign of prediabetes. This condition, known as acanthosis nigricans, is often an early warning sign of diabetes or prediabetes.
Although it can sometimes develop in people with no underlying health problems, it is often associated with insulin resistance. If you notice these patches, it is important to see a doctor for further evaluation.
Extreme Hunger and Unexplained Weight Loss

In diabetes, the inability of cells to absorb glucose properly means that—even after eating—the body still craves energy. This can result in constant hunger and, paradoxically, weight loss despite an increased appetite. These are classic hallmarks of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Skin Changes and Gum Disease

Several articles and even sensationalist headlines in tabloids mention unusual skin findings (like acanthosis nigricans—a dark, velvety discoloration often found on the neck or underarms) and gum disease as potential early indicators. Medical research does support that prolonged high blood sugar can lead to skin changes and periodontal issues, but these manifestations tend to occur later in the course of the disease rather than as initial symptoms.
Fatigue and Blurred Vision

Elevated blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to deliver energy to cells, leading to persistent fatigue. Additionally, high glucose can alter the fluid balance in the lenses of the eyes, causing temporary blurred vision. These symptoms are well documented in clinical practice.
Frequent Urination and Excessive Thirst

Both the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the Cleveland Clinic confirm that polyuria (frequent urination) and polydipsia (increased thirst) are among the most common early signs of high blood sugar. When excess glucose spills into the urine, your kidneys work overtime to excrete it, leading to dehydration and a persistent need to drink fluids.
Skin Tags
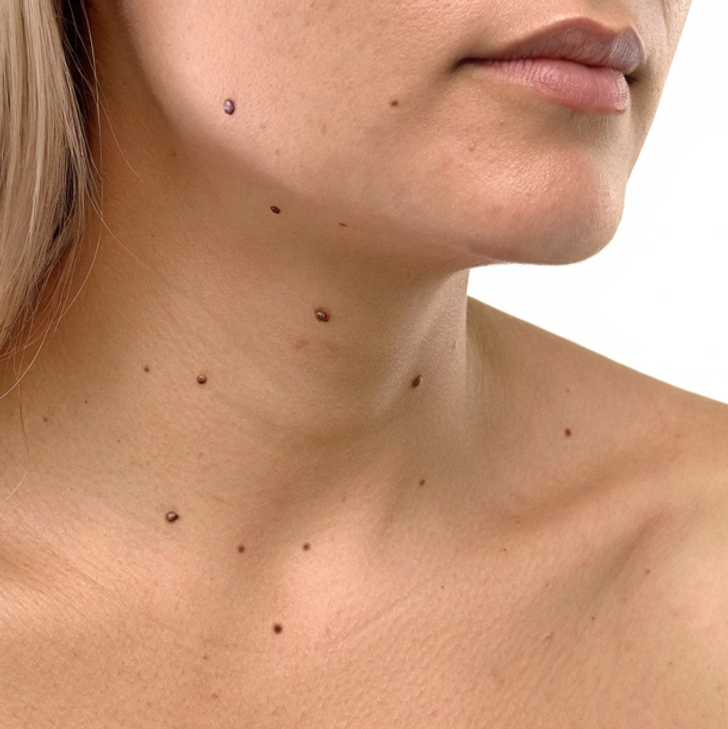
Skin tags are common, benign skin growths that can appear on different parts of the body. Some are firmly attached to the skin, while others hang from a small stalk. Medically, these growths are called acrochordons.
Although skin tags can form anywhere on the body, they are most commonly found on the eyelids, neck, armpits, and groin. While they are harmless, having a large number of them may indicate an underlying medical condition, such as type 2 diabetes. If you notice an unusual number of skin tags, you may want to see a doctor to determine if you need to be tested for diabetes.
Slow-Healing Cuts and Frequent Infections
Chronic hyperglycemia can impair circulation and weaken the immune system. As a result, small cuts or infections (such as skin or urinary tract infections) may take longer to resolve.
Itchy Skin
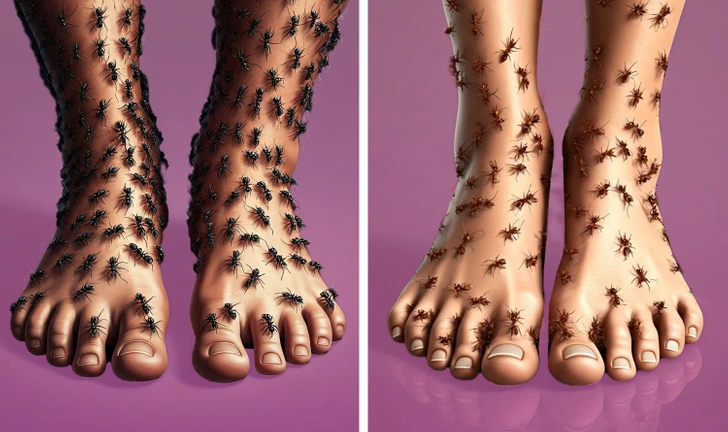
Tingling and numbness in the extremities may be a sign of prediabetes. Elevated blood glucose levels can damage small nerves, leading to a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. In addition to tingling and numbness, this condition can also cause a burning sensation in the hands, arms, and feet or the sensation of socks bunching up under the toes.
Early detection and treatment of prediabetes can help reduce these symptoms and lower the risk of developing diabetic neuropathy.
6 Non-Obvious Signals Your Body May Be Using to Warn You of Health Issues
Bad or Fruity Breath
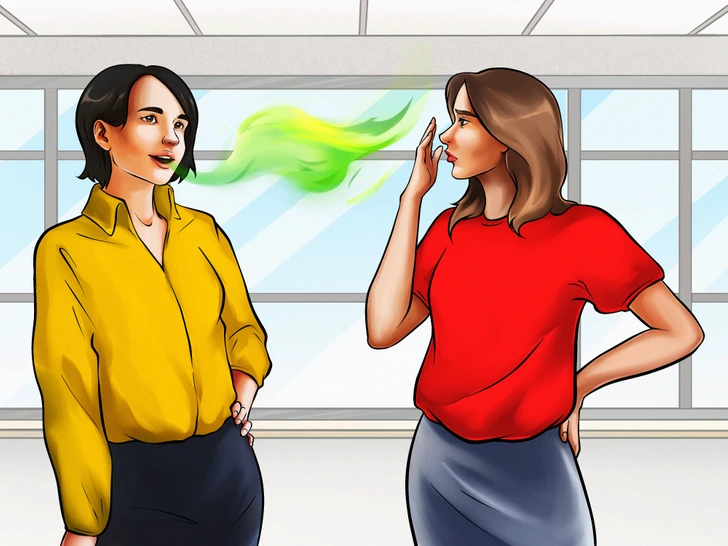

A fruity or acetone-like breath is most often associated with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a severe complication more typical in type 1 diabetes when insulin levels fall dangerously low. While several media reports highlight “smelly breath” as an early warning, it is generally a sign of an acute state rather than a subtle, early marker of diabetes.
Evaluating the Claims: What Does the Evidence Say?
When evaluating “warning signs” lists from various sources, it is important to note the following:
- Core Symptoms Are Consistent: Medical authorities and large organizations (such as the ADA and the American Heart Association) consistently highlight frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision as the primary early indicators of diabetes.
- Supplementary Signs Require Context: Other signs—such as skin changes, gum disease, and mood alterations—may indeed occur in diabetic patients but typically in conjunction with the core symptoms or as complications of long-standing high blood sugar.
- Sensationalism vs. Scientific Rigor: Some media outlets tend to present dramatic versions of these symptoms (for example, attributing “smelly breath” or “aggression” solely to diabetes) without the nuance that these can result from many factors. It is always best to cross-reference such claims with peer-reviewed research or established medical guidelines.
What Should You Do If You Notice These Signs?
If you observe one or more of the core warning signs—especially if you are at high risk due to factors like age, obesity, family history, or certain ethnic backgrounds—it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider. A professional evaluation typically involves:
- Blood Tests: Screening tests like the fasting plasma glucose test, the oral glucose tolerance test, or an HbA1C test are essential for confirming the diagnosis.
- Lifestyle Assessment: Your provider will also evaluate your lifestyle and overall health to recommend changes that can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Early detection and management of diabetes can reduce the risk of serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy.
Taking these steps is supported by guidelines from reputable organizations.
While headlines may urge you to “watch out” for a long list of potential symptoms, the most reliable early warning signs of diabetes remain frequent urination, excessive thirst, increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and unexpected weight loss. Other symptoms—such as specific skin changes or mood alterations—can occur but are usually secondary and should be considered alongside the core signs.
The key takeaway is to remain vigilant about changes in your health. If you are at risk or notice a combination of these symptoms, seek professional advice promptly. Early diagnosis and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve health outcomes and help manage or even prevent the complications associated with diabetes.
By staying informed and consulting with healthcare professionals, you can cut through sensational claims and focus on evidence-based strategies to protect your health.
You might be surprised to learn how quitting coffee could affect your body. From unexpected fatigue to unusual cravings, your body has its own way of responding. Curious about what to expect? Stay tuned!
15 Alarming Signs Your Body Needs Help
Your body is a remarkable machine, constantly working to keep you healthy and functioning. But sometimes, it needs a little help understanding its own signals. Here are 14 signs your body might be trying to tell you something important:
THIS CONTENT IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND SHOULD NOT BE CONSIDERED A SUBSTITUTE FOR PROFESSIONAL MEDICAL ADVICE. ALWAYS CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR OR A QUALIFIED HEALTHCARE PROVIDER FOR GUIDANCE REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONCERNS.
1. Persistent Fatigue
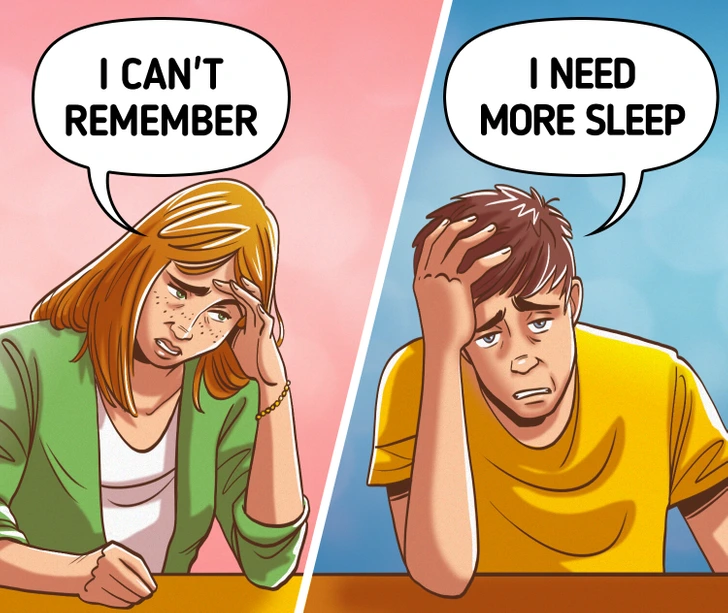

Feeling tired all the time, even after a good night’s sleep? In some cases, it could be a sign of iron deficiency, thyroid problems, or even sleep apnea.
2. Dandruff and hair loss
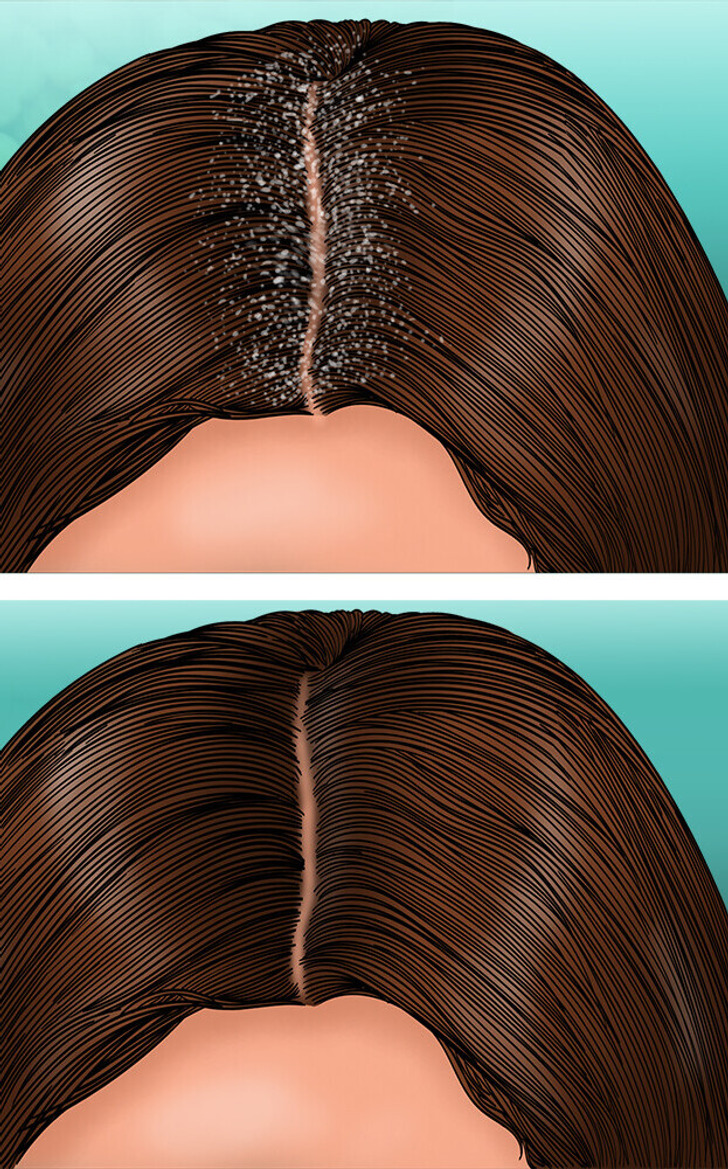

Flaky scalp can be a common problem and in combination with hair loss can be a sign of a lack of important vitamins and nutrients. Low levels of Zinc, Vitamins B2, B3, B6, and B7, as well as Iron may be contributing to this common problem.
3. Wrinkly hands and fingers

Wrinkles on our bodies are a normal, healthy sign of aging. And we usually get wrinkled fingers when we spend a lot of time in water. But your body may be sending you a warning when your hands start to look more wrinkled and lose elasticity faster than other parts of your body. Wrinkling your fingers without getting out of the water could mean dehydration, poor circulation, or a problem with your thyroid.
4. White patches on the tongue
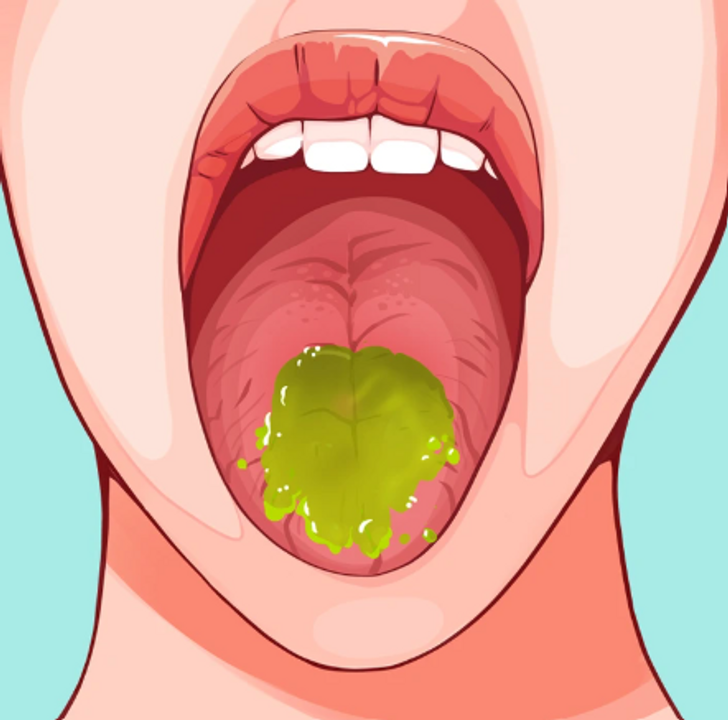
A healthy tongue is usually pink. If you notice white patches appearing on your tongue, it could be a sign of oral thrush, which is very common in people with diabetes. The patches could also be a sign of inadequate oral care, so improving your oral hygiene could help the problem.
5. Horizontal lines on your neck
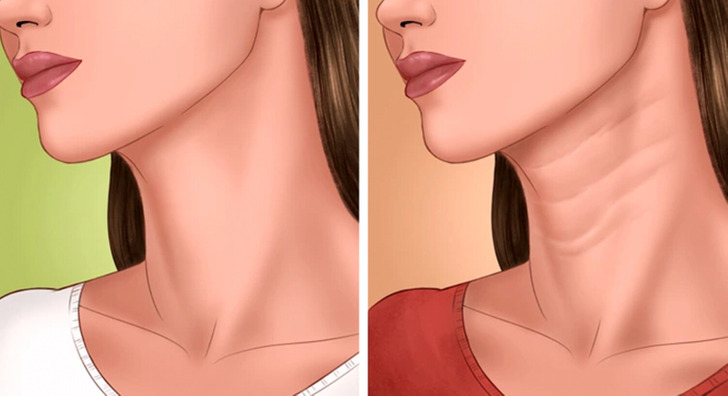
Estrogen, which is essential for maintaining bone strength, decreases in postmenopausal women. A surprising sign of bone weakness and loss of bone density is the appearance of deep neck wrinkles. This indicates a higher risk of fractures. Calcium and vitamin D supplements may be beneficial in the prevention of osteoporosis.
In addition, these neck wrinkles may indicate an underactive thyroid gland. If left untreated, worsening thyroid conditions can manifest themselves in neck changes such as wrinkles and scaly skin. Knowing how to look for these signs and talking to a doctor can help get underlying problems addressed early.
10 Body Signs That Can Mean Your Blood Sugar Level Is Not Right
6. Skin rashes
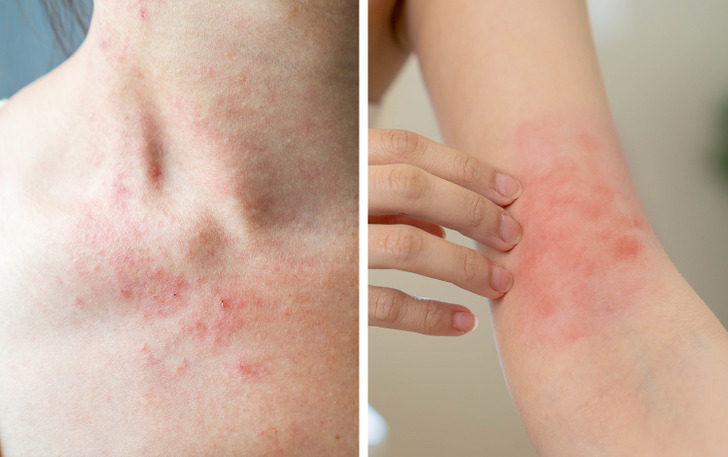
Red, itchy skin is usually a sign of eczema, but sometimes rashes along with a fever can be caused by infections or touching certain plants. Even if they don’t look very serious, the patches can become infected, so it’s a good idea to get them checked out by a healthcare professional.
7. Swollen ankles
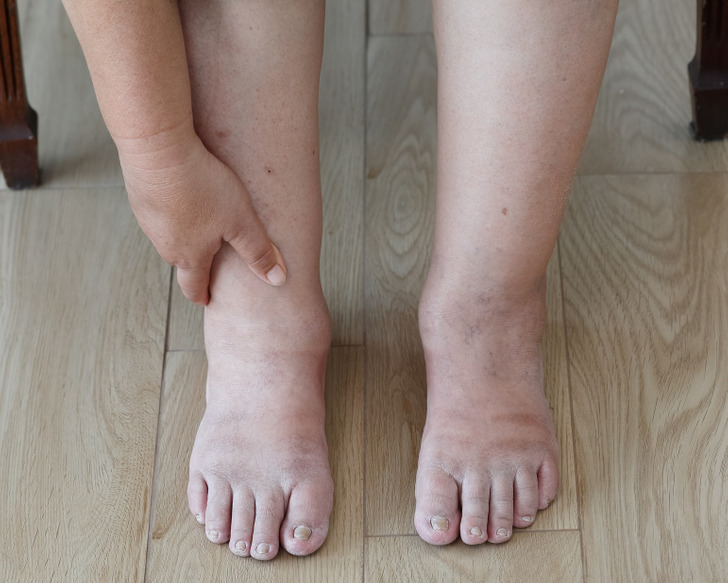
Swollen ankles are a common sign of pregnancy, but if you are not expecting a baby, they can mean poor circulation, heart problems, or an underactive thyroid. A less serious cause of this symptom is eating too much salt, which can lead to water retention.
8. Dry eyes
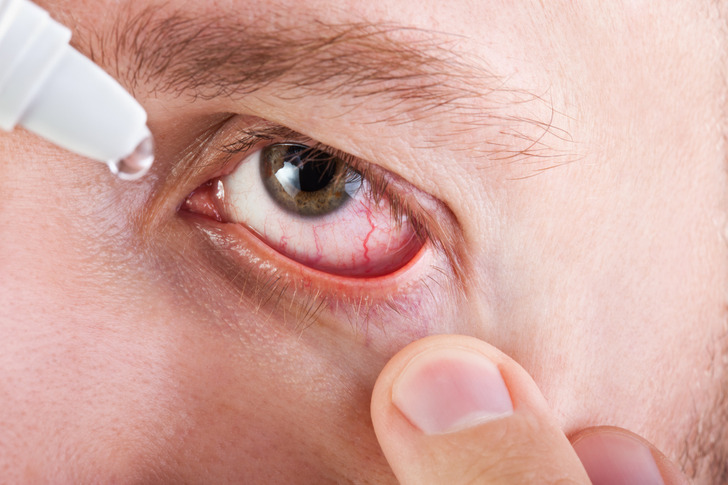
This can cause burning, inflammation, and damage to the eyes. The dryness may be caused by aging or certain medications, but it may also be a sign of Sjogren’s syndrome. Sjogren’s is often associated with dry mouth and is a disorder of the immune system.
9. Bloating
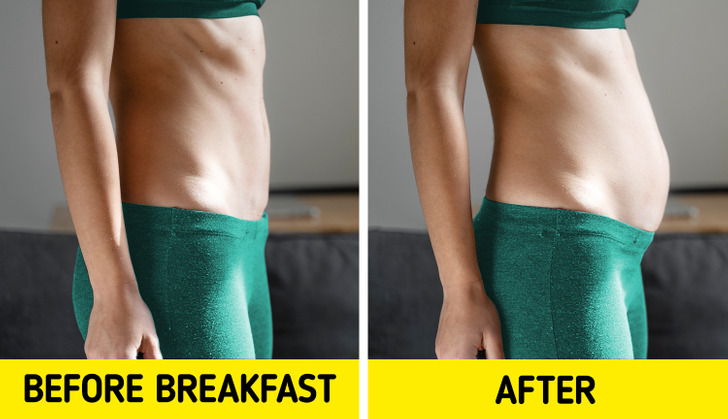
A little gas after a meal is usually nothing to worry about, but it can be a sign of food sensitivity. Eating foods you’re allergic to (even if you don’t know it) causes a lot of gas to be released in your stomach. The most common foods that cause this are wheat and gluten.
10. Unexplained bruises
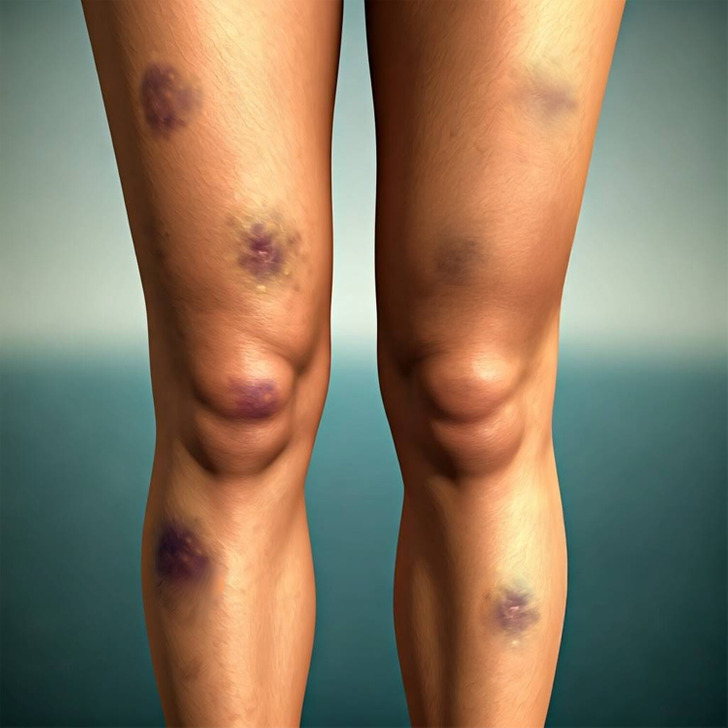
If you keep getting bruises in random places and can’t remember bumping into anything, it might be a good idea to see your doctor. Random and easy bruising could mean a simple vitamin deficiency, but it could also be a sign of something more serious, such as a blood clotting disorder.
11. Constant thirst
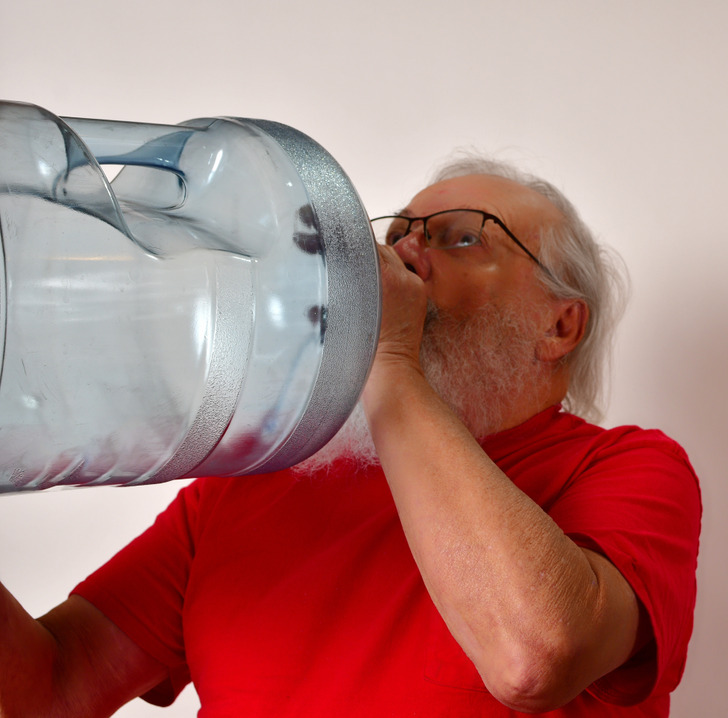

Keeping your body hydrated and drinking plenty of water is always important, but feeling thirsty all the time is a typical symptom of prediabetes. Other common symptoms include fatigue and frequent urination as a result of constant thirst.
12. Random muscle twitches
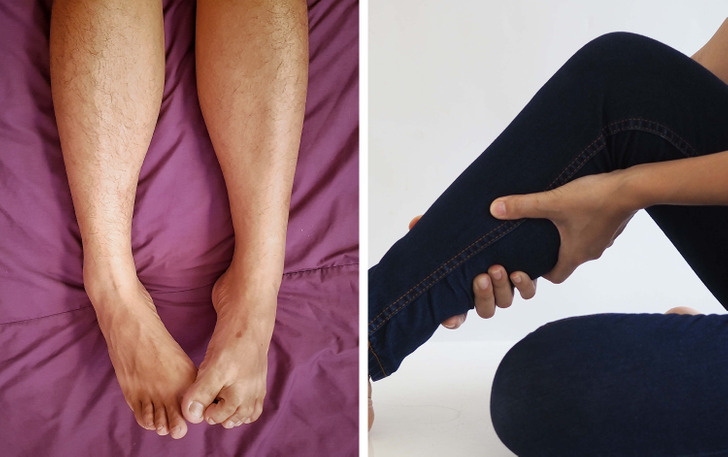
Muscle spasms can have many causes, including physical activity, stress, dehydration, and lack of sleep. In more serious cases, it may indicate a neurological disorder or kidney disease.
13. Puffy or even swollen eyes
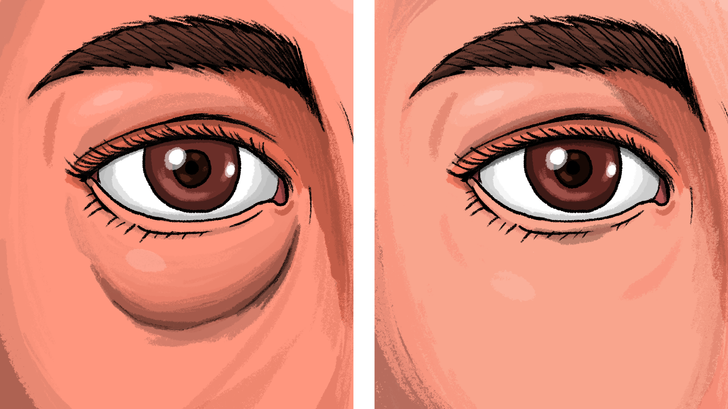
If you don’t have an infection or allergies and still have a puffy eye, the most likely culprit is too much salt. Excess salt causes your body to retain water, which leads to swelling, including around the eyes. To combat this, reduce your salt intake and consider increasing your potassium levels. Other possible causes of puffy eyes include Grave’s disease, a blocked tear duct, smoking, or lack of sleep.
Once you identify the cause, begin treatment with simple remedies such as cold compresses, tea bags, or facial massage. However, if the swelling persists despite your efforts, it’s important to see a doctor for further evaluation and treatment.
14. Snoring
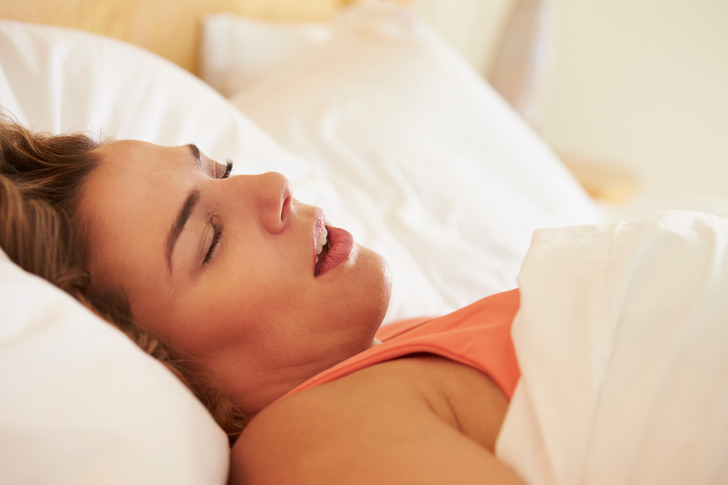

While annoying to your partner, snoring is often harmless to your body. Less commonly, it can be a sign of OSA (obstructive sleep apnea). OSA requires medical attention, and your doctor may prescribe a medical device to help you sleep and breathe better at night.
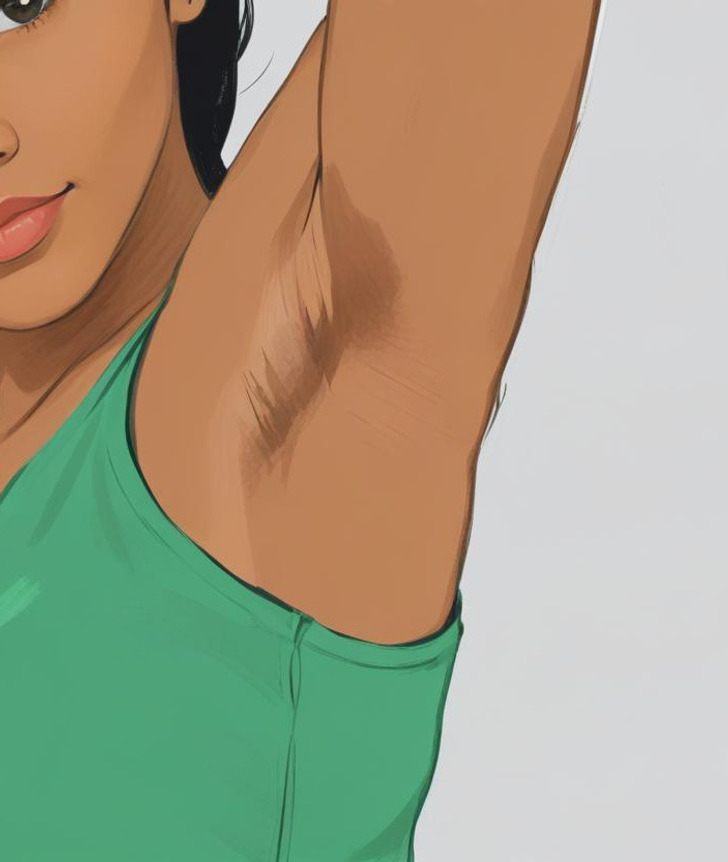
15. Dark armpits
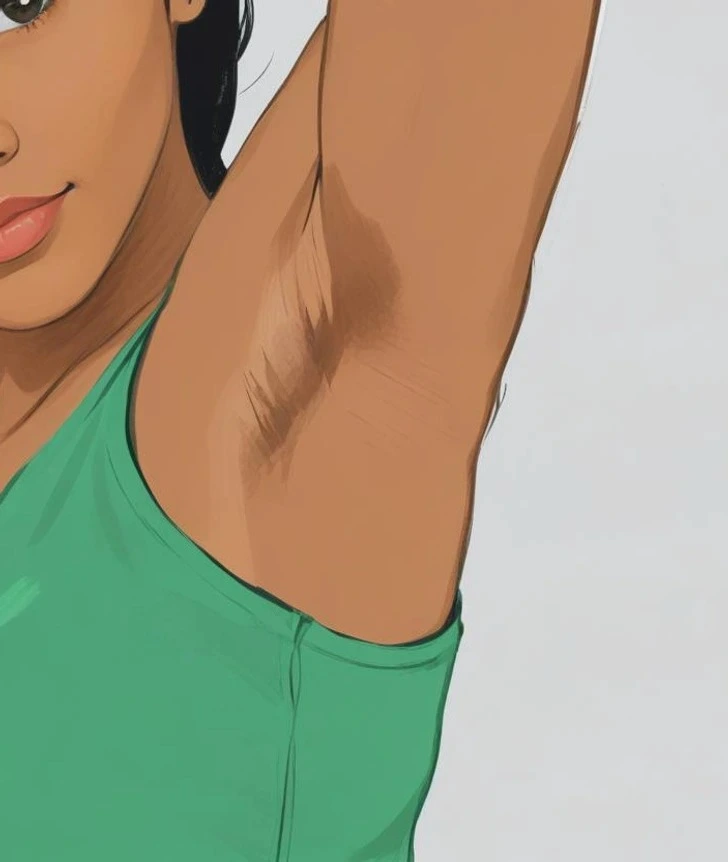

Dark armpits can be an indicator of a condition known as acanthosis nigricans, which is often associated with diabetes or insulin resistance. This skin condition manifests as dark, velvety patches in body folds, including the armpits, neck, and groin. The presence of these dark areas can signal an underlying metabolic issue, as they typically occur in individuals who may be pre-diabetic or have obesity. If you notice such changes in your skin, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance. Recognizing these signs early can be crucial for managing your health effectively!
But what if your body is trying to tell you something much more alarming? Here are five red flags you should never ignore when it comes to your colon health.
12 Signs Your Body Could Be Sending About Lactose Intolerance
Have you ever experienced stomach troubles without knowing why? It might be your body’s way of signaling an issue with lactose. Lactose intolerance affects millions of people, yet many remain unaware that their symptoms stem from an inability to digest dairy properly.
Lactose intolerance arises when the small intestine does not produce sufficient lactase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products.
In this article, we’ll highlight 12 key signs that could indicate your body is struggling with lactose intolerance. Recognizing these warning signals can help you take steps toward managing your discomfort and improving your well-being.
CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE OF MEDICAL ADVICE.
SEEK GUIDANCE OF YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.
Abdominal pain
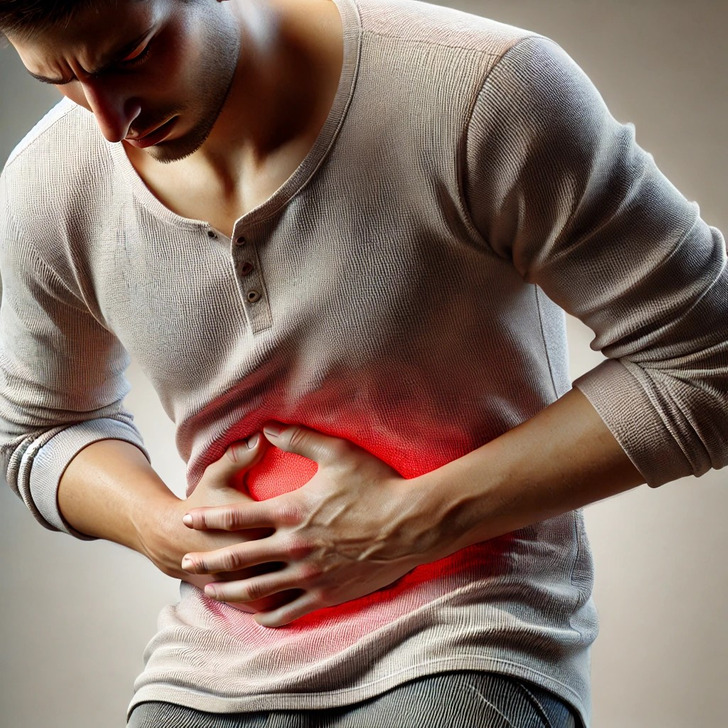
Perhaps the most common symptom that could indicate something wrong is abdominal pain or discomfort. It might be that nagging stomach pain after eating ice cream or cheese. It could be your body reacting to undigested lactose. When lactose isn’t properly broken down, it moves into the colon, where bacteria ferment it, producing gas and acids. This leads to bloating, pressure, and those painful cramps you just can’t shake.
Nausea
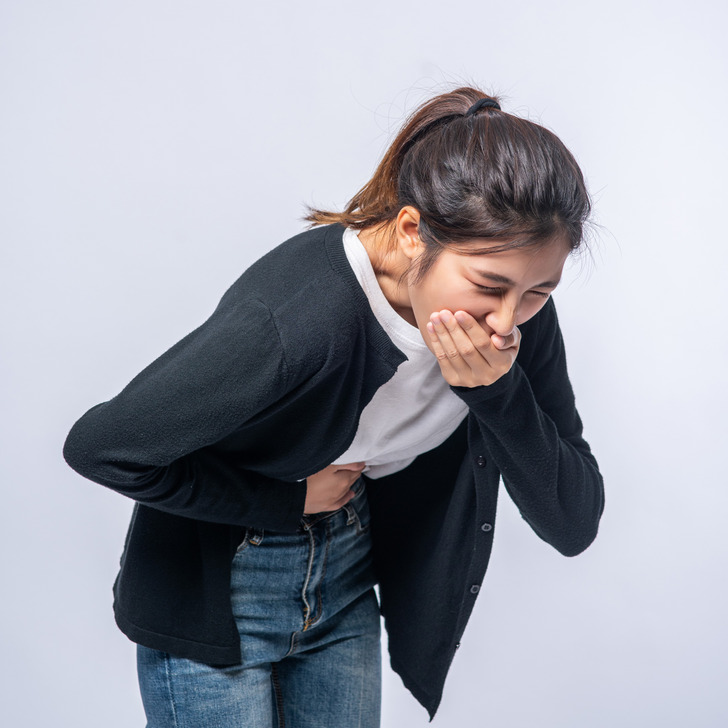

If dairy leaves you feeling queasy, you’re not alone. Some individuals experience nausea, and in more severe cases, even vomiting after consuming lactose. This happens due to the irritation and discomfort lactose causes in the digestive tract.
Feeling tired

Constantly feeling drained? Lactose intolerance might be playing a role. Digestive discomfort disrupted gut health, and systemic inflammation caused by undigested lactose could contribute to fatigue and sluggishness. Managing your symptoms could mean the difference between feeling exhausted and feeling energized.
Brain Fog

Do you struggle with forgetfulness, lack of focus, or mental sluggishness after eating dairy? Some individuals with lactose intolerance report experiencing brain fog, which can make it difficult to concentrate or think clearly. While the exact cause isn’t fully understood, it may be related to inflammation triggered by undigested lactose or gut-brain interactions affecting cognitive function.
Indigestion

Persistent discomfort after meals, including feelings of fullness, burning, or mild pain in the upper abdomen, might be linked to dairy consumption. Indigestion from lactose intolerance occurs when your body fails to break down lactose properly, leading to irritation in the stomach and intestines.
Mouth ulcers
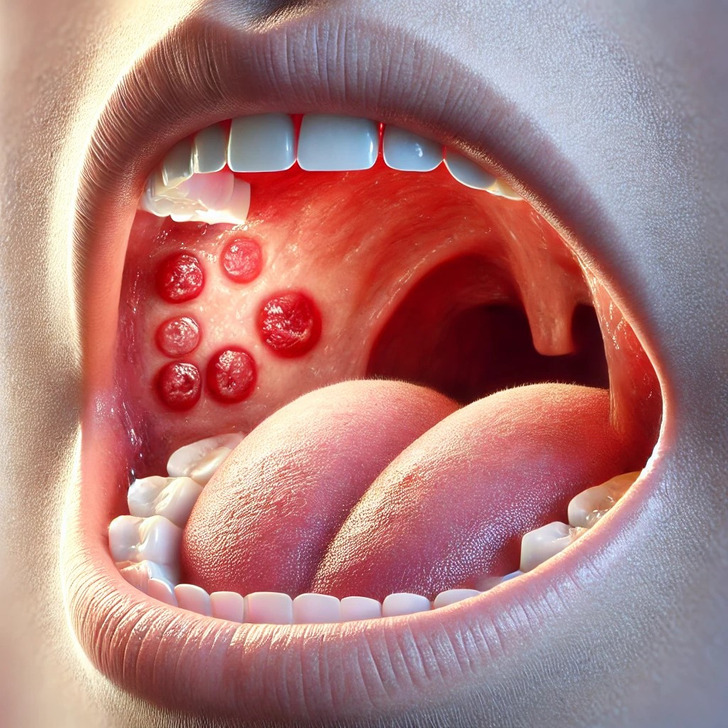
Mouth ulcers are not commonly linked to lactose intolerance. However, some case studies have reported mouth ulcers in individuals with lactose intolerance, though the exact mechanism remains unclear. It’s possible that these symptoms may be related to other underlying conditions or food sensitivities. If you frequently experience mouth ulcers, seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause.
Swelling

While not widely recognized as a direct symptom of lactose intolerance, some individuals report skin-related issues, such as rashes or eczema, after consuming dairy products. But, it’s important to distinguish between the two, as a milk allergy can lead to more severe reactions.
- Common symptoms include:
- Rashes, hives, or redness that are often itchy or inflamed.
- Facial swelling, particularly around the lips, eyes, and face.
- Wheezing, coughing, or a tight sensation in the throat.
- Swallowing Difficulties
Severe reactions can escalate to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening emergency marked by throat swelling, difficulty breathing, a rapid pulse, and a drop in blood pressure. Anaphylaxis typically develops within minutes of consuming a trigger but can sometimes be delayed.
Diarrhea or constipation

Do you have loose stools after consuming dairy? This happens because undigested lactose pulls extra water into the intestines through osmosis, disrupting stool consistency. If you notice frequent bouts of diarrhea after enjoying milk-based products, it might be time to rethink your diet.
While diarrhea is a more common reaction, some people experience constipation instead. Scientists believe that lactose intolerance may sometimes slow gut motility or alter gut bacteria, making digestion sluggish. If dairy leaves you feeling blocked up, it might be worth investigating your lactose intake.
Bloating
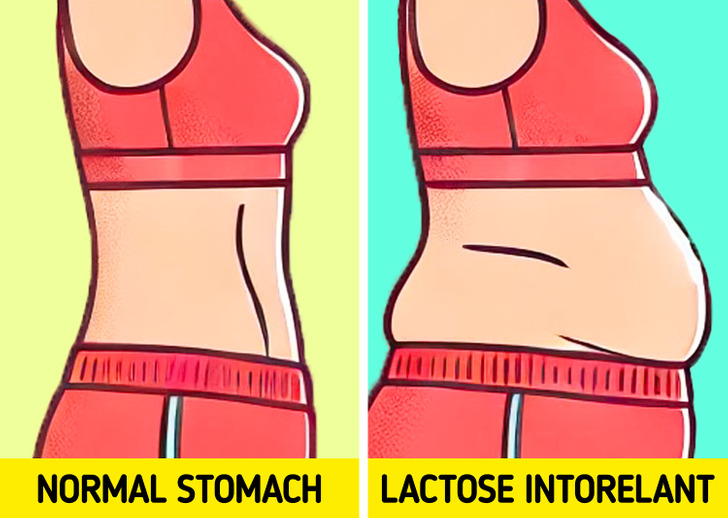
If you feel like your stomach is about to burst, maybe it is a warning sign that you might be lactose intolerant. Bloating is a classic sign of lactose intolerance. The gas produced by bacteria fermenting undigested lactose can make your abdomen feel swollen and uncomfortable. The severity varies based on how much lactose you consume and how sensitive your body is.
Headache

Struggling with unexplained headaches? Some individuals report migraines or persistent headaches after consuming dairy. While the connection isn’t fully understood, experts suspect that gut inflammation and digestive distress could trigger headaches in sensitive individuals.
Flatulence
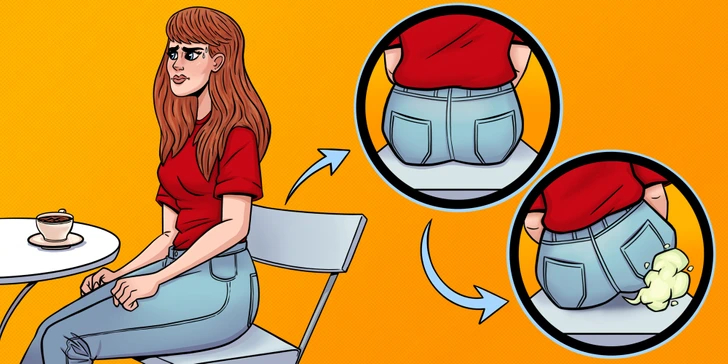
Excessive gas isn’t just embarrassing. It’s a telltale sign that your body is struggling with lactose. When bacteria in the colon break down lactose, they produce hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide, leading to increased flatulence. The more dairy you consume, the more gas your gut has to handle.
Muscle and joint pain
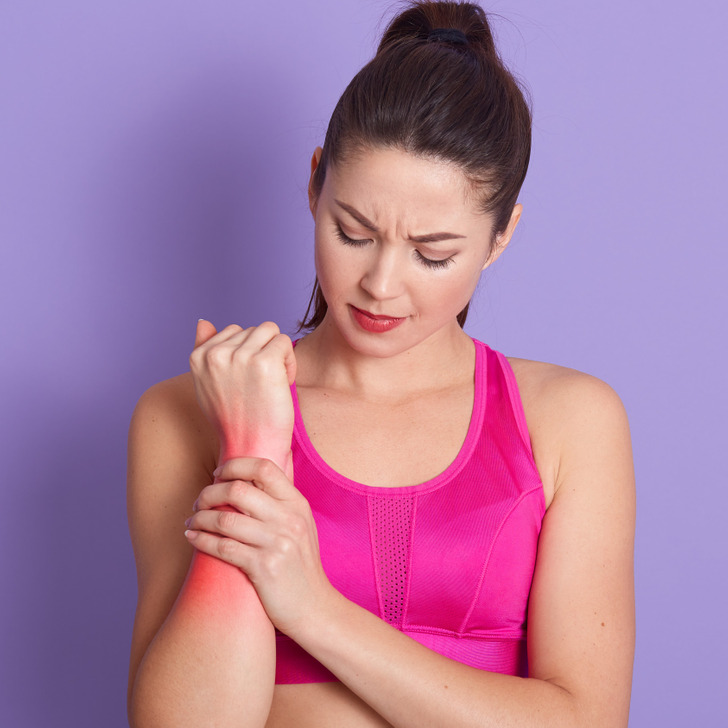

Although this symptom is rare, some people report muscle or joint discomfort after consuming dairy. While this isn’t a widely recognized symptom, researchers speculate that lactose intolerance may trigger mild inflammation, potentially leading to aches and pains in certain individuals. If you suspect a link, try eliminating dairy and see if your symptoms improve.
Furthermore, if you’re experiencing symptoms of lactose intolerance, it could be helpful to explore whether gluten intolerance might also be a contributing factor.






































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(749x0:751x2):format(webp)/Celia-Strauss-honor-1-011426-e2d70959dae04b558475f2bef7271942.jpg?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)


